AI Model Proliferation
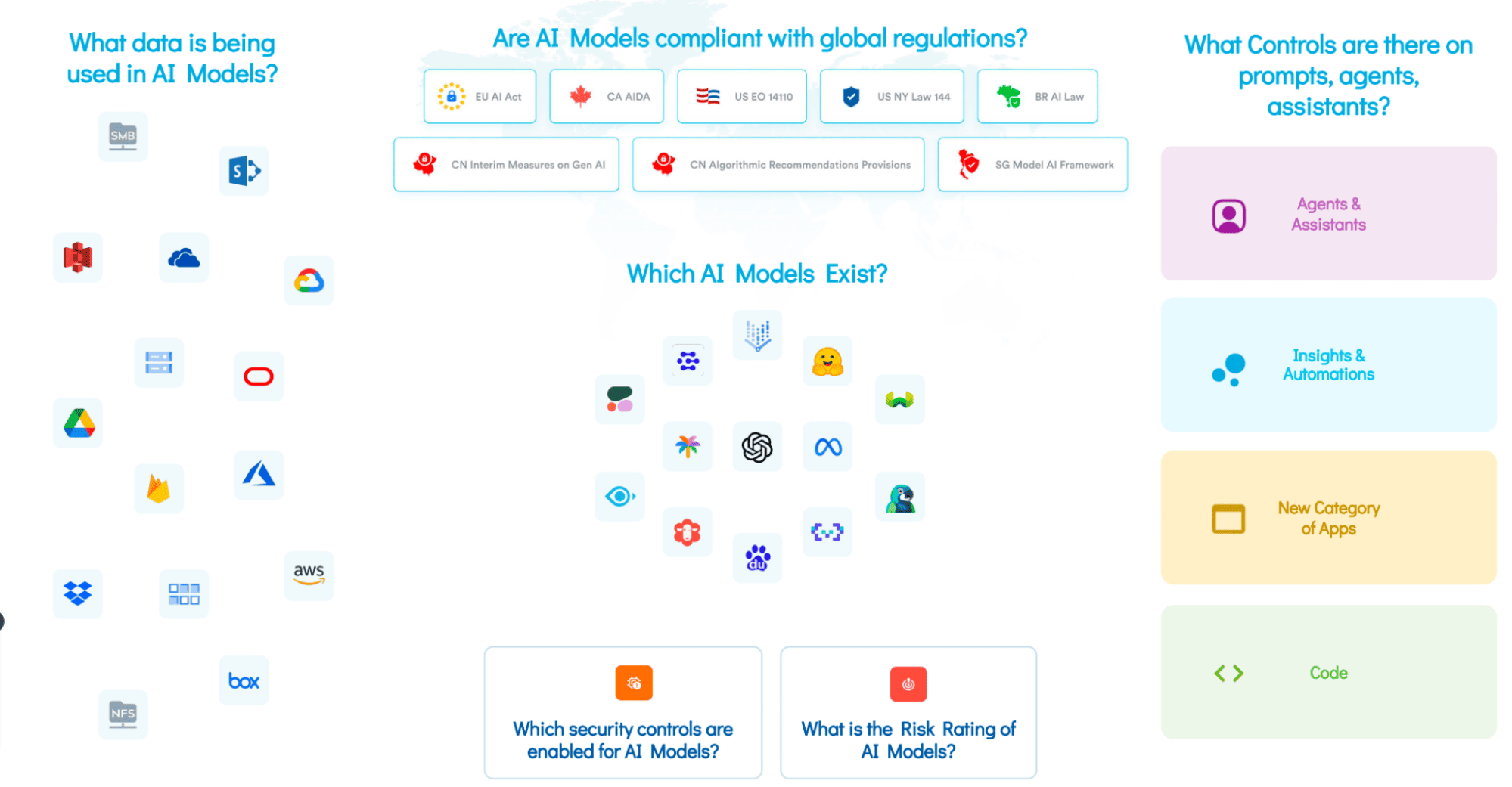
Large organizations aren’t limited to a single AI model to accelerate their operations and growth. In fact, a single organization may be using a number of LLMs, either directly deployed by the developers or accessed through a third-party (SaaS) application. It becomes challenging for organizations to keep a single inventory of all the AI models, let alone a catalog of Shadow AI. The Shadow AI is a bunch of ad-hoc or unsanctioned AI systems that exist in the environment but without proper IT governance. The lack of visibility into existing AI models in the environment puts AI governance, data security, privacy, and compliance at serious risk.
Inherent Risks in AI Models
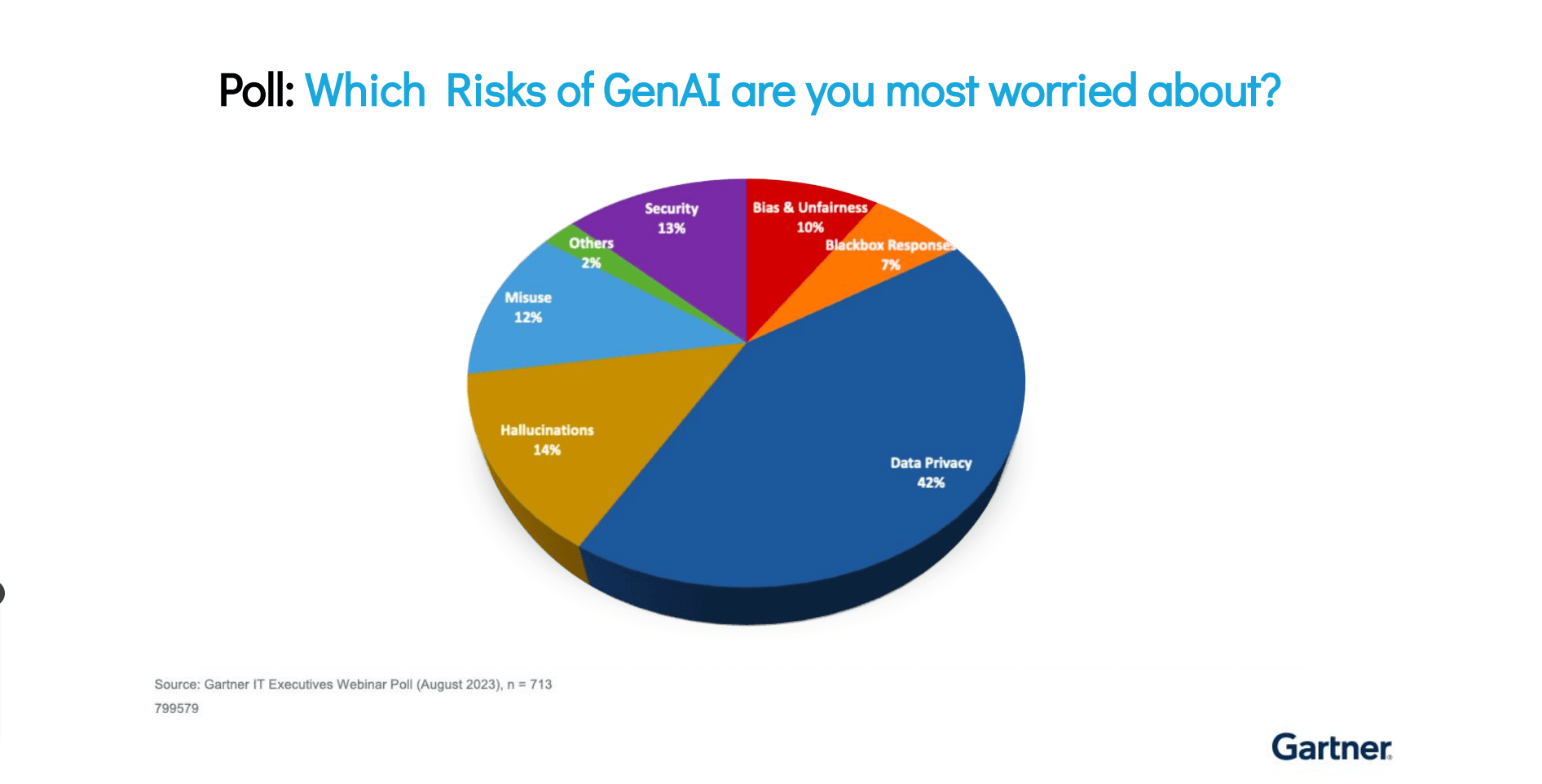
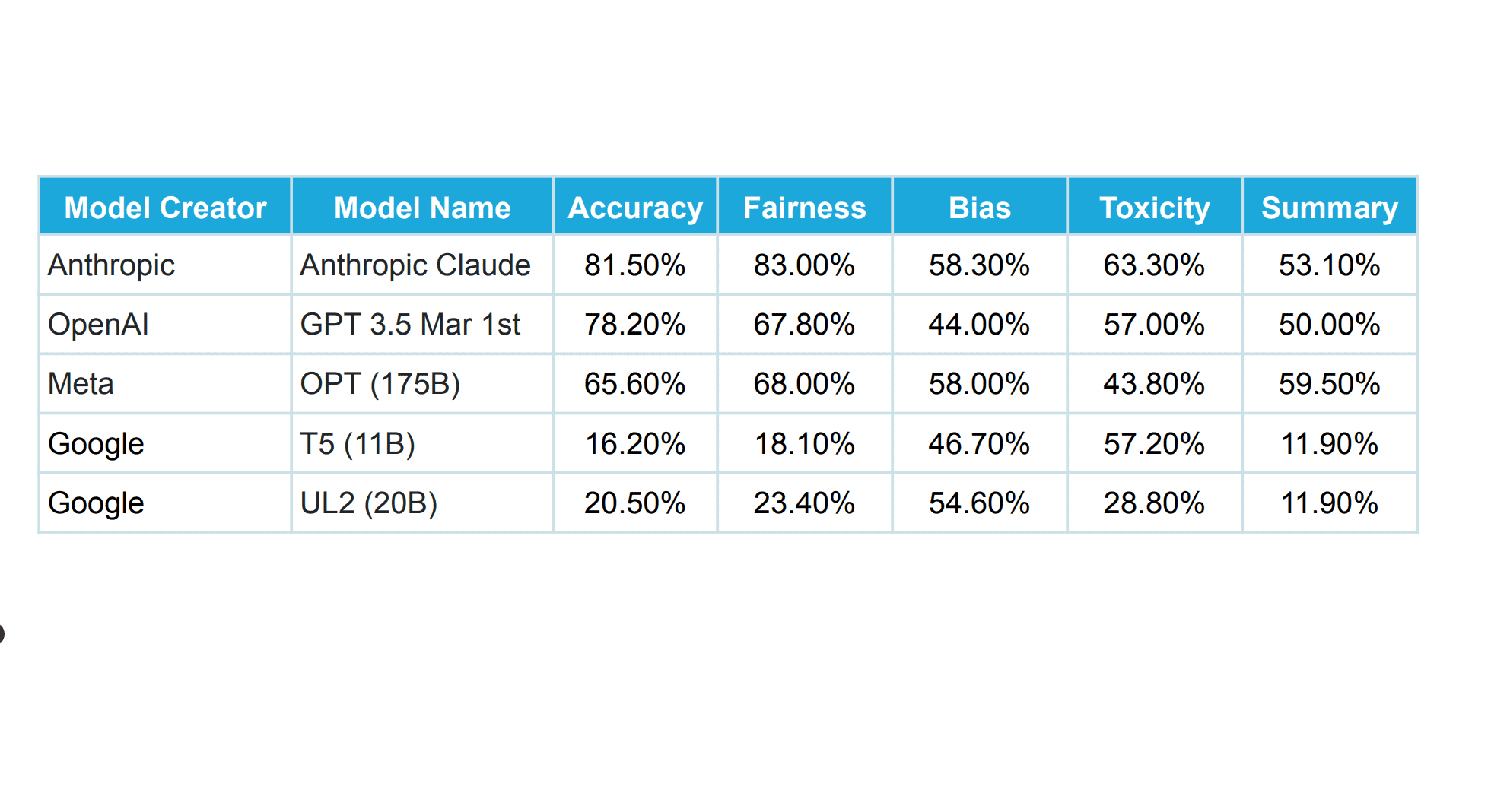
Organizations currently don’t have a standard AI risk assessment framework. This makes it difficult for teams to get an accurate picture of the risks inherent in their AI models. With no concrete way to accurately assess risks, AI models tend to face issues like toxicity, bias, hallucination, and discrimination, to name a few.
Security Gaps in Models
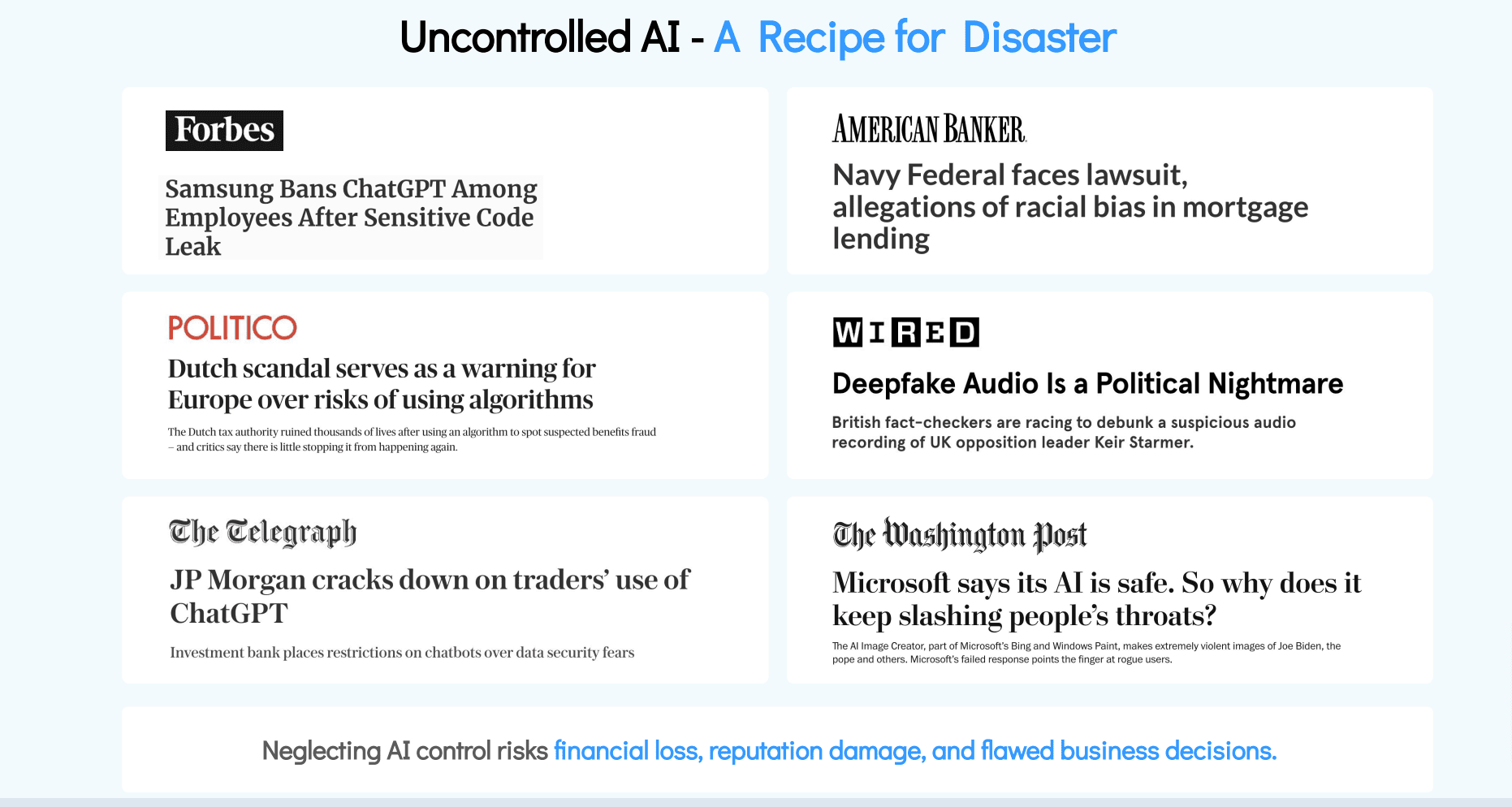
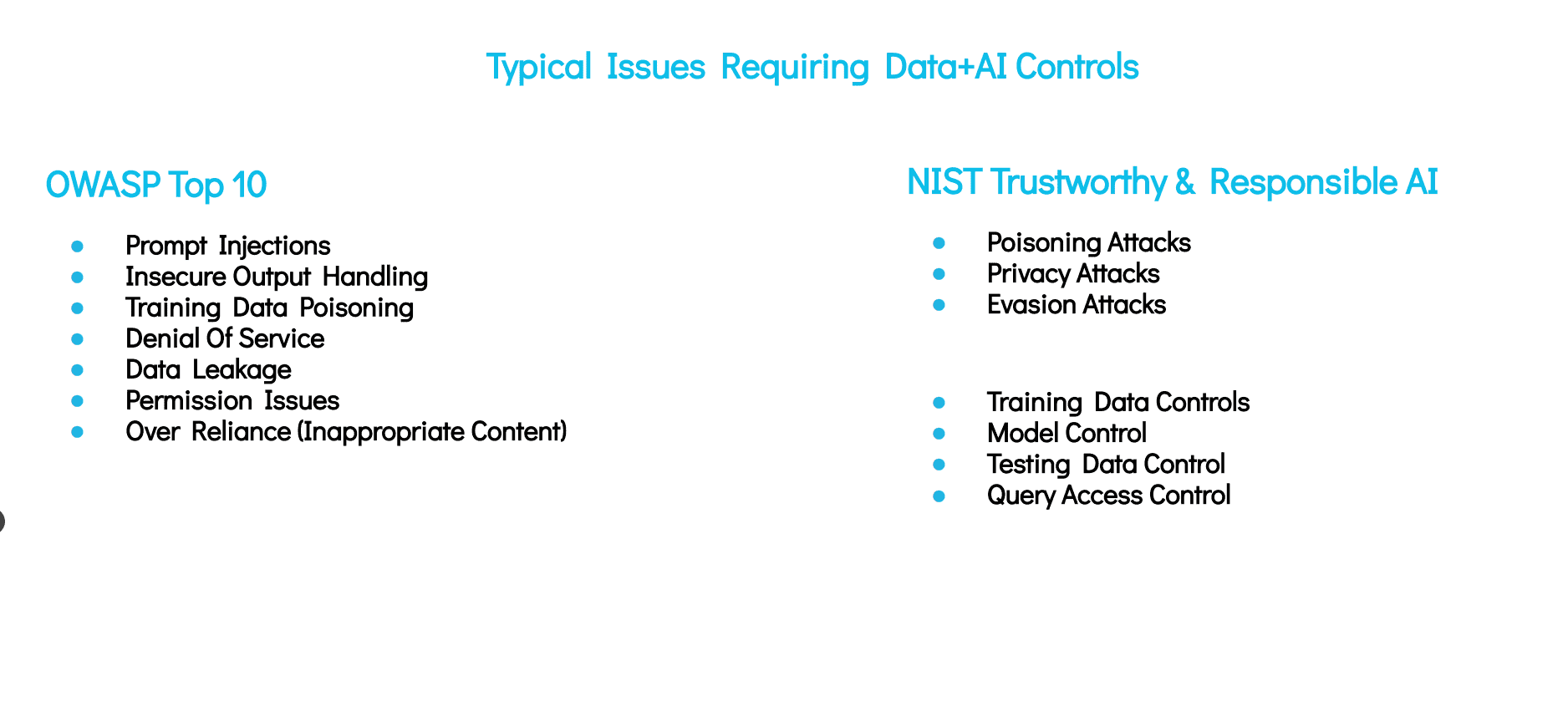
AI models are different from traditional data systems. At a time, a single model can have a considerable volume of compressed information stored in it. The integrity or the security of the model can severely be compromised if organizations fail to make sure appropriate security or access controls are established in and around the models. Security gaps can render AI models incapable of safeguarding against manipulation, data leakage, or other malicious cyber threats.
Unprotected Training Data
Apart from AI models, it is increasingly important to protect the data that is flowing into the AI models, i.e., the training data. AI models require training data to work efficiently and deliver accurate results. It is important that teams should have a clear understanding of what data needs to be allowed for training the AI model and what type of data should be restricted, such as sensitive data. When teams lack the insights into which data is being leveraged to train the model, concerns may arise around access entitlements. Needless to say, inadequate access entitlements further result in potential sensitive data leakage and unauthorized access to training data.
Unguarded AI Agents and Prompts
Security, governance, and privacy controls shouldn’t be limited to AI models or training data alone. In fact, these controls should be extended to the prompts and agents. It is critically important that organizations place guardrails around AI prompts and agents, as leaving these critical areas could open doors to harmful interactions with the models, putting users’ safety and ethical principles at risk.
Ever-Changing Regulatory Maze
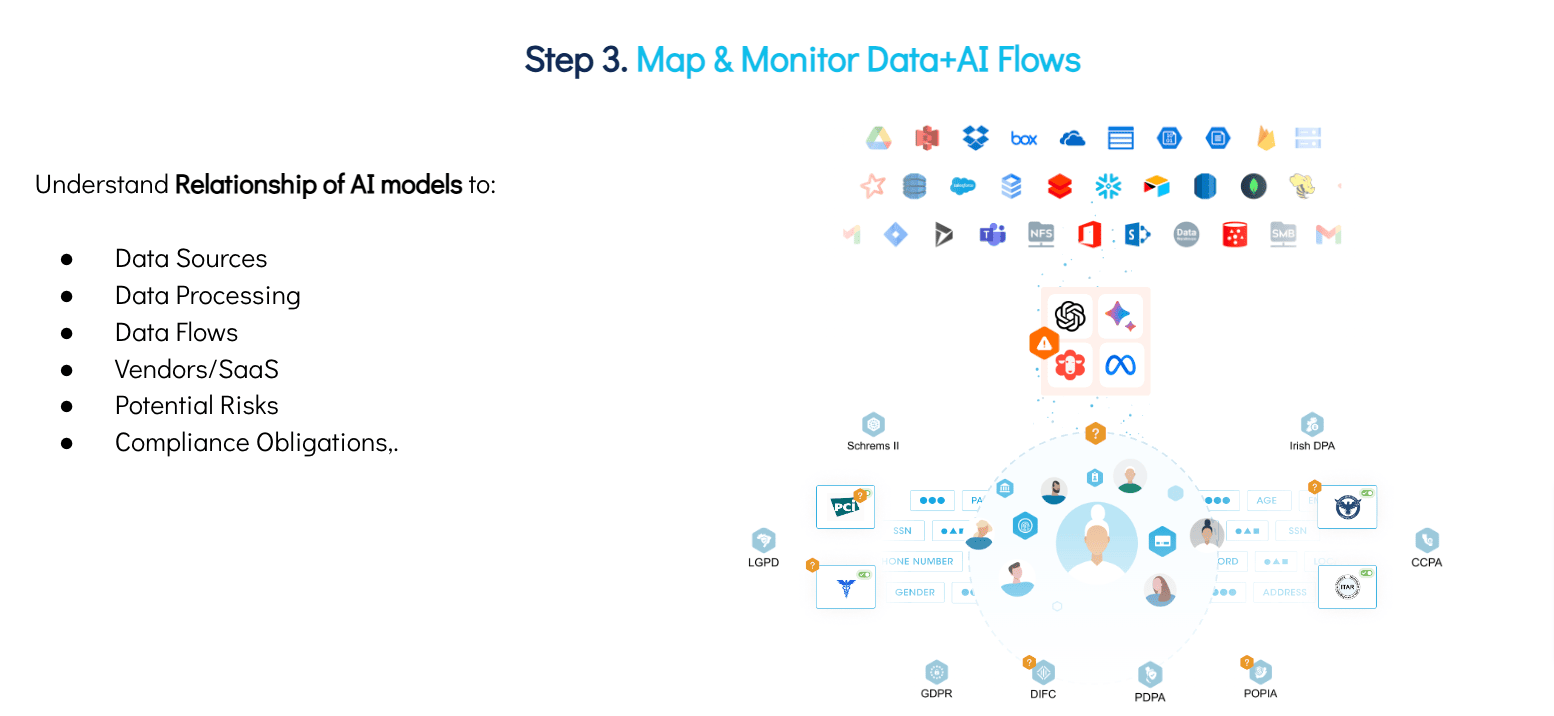
There are tons of AI regulations that are coming through. North America recently introduced the AI governance framework or a set of guidelines in the form of an AI Executive Order. Similarly, the EU AI Act is yet another comprehensive AI law that has turned heads when it was first introduced. Similarly, new regulations and standards will be coming and receiving amendments as the technology further advances. To comply with these regulations or standards concerning AI, it is imperative for organizations to have complete visibility around their AI models, training data, prompts, access entitlements, and processing policies. Without these crucial insights, it would be difficult to establish appropriate controls, let alone ensure compliance.
What is an AI TRiSM Approach?
AI TRiSM stands for Trust, Risk, and Security Management. It is a comprehensive framework that enables organizations to ensure “AI model governance, trustworthiness, fairness, reliability, robustness, efficacy, and data protection,” as defined by Gartner. In fact, as per Gartner, organizations that operationalize secure and trustworthy AI will achieve a 50% increase in their AI adoption and business goal attainment.
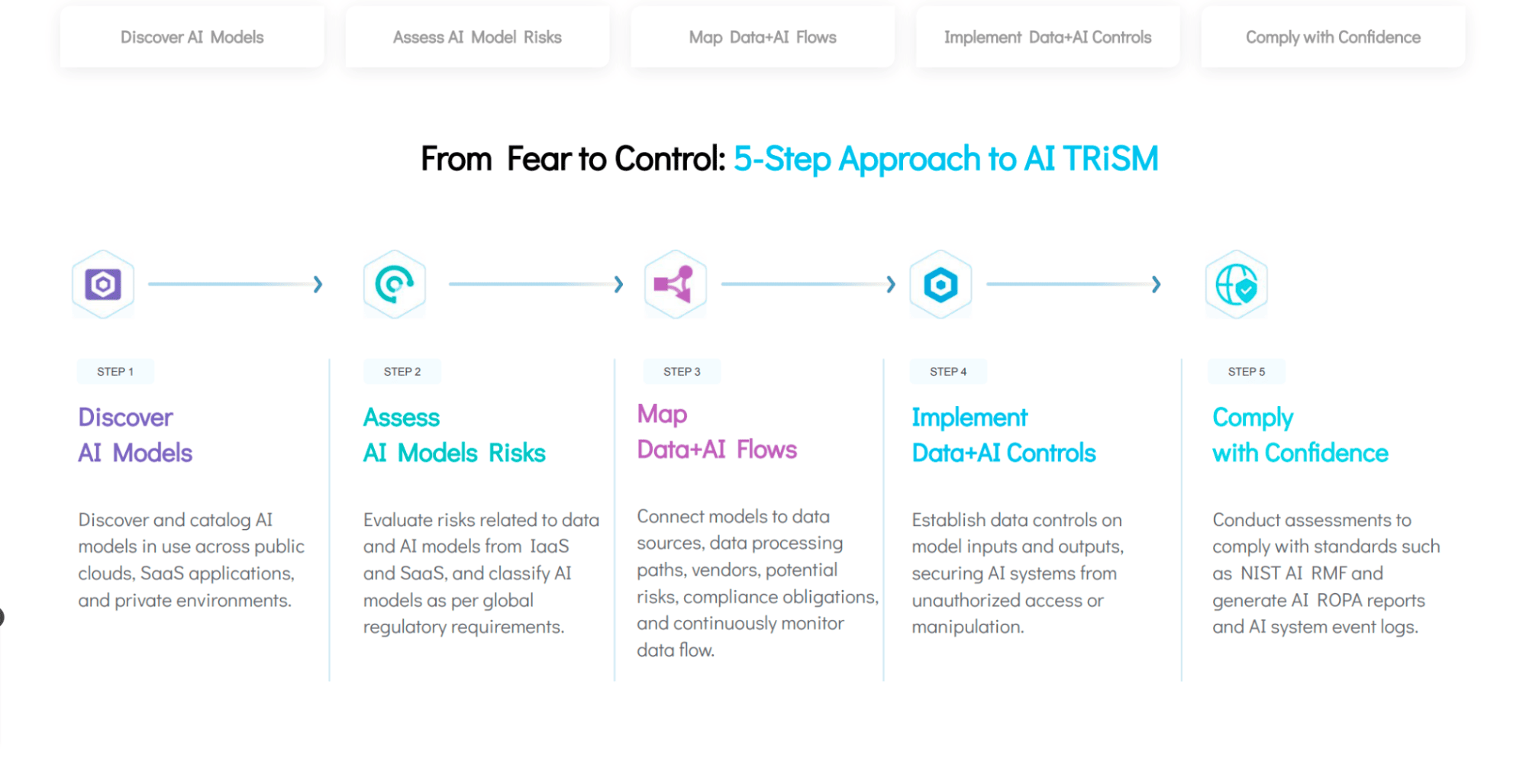
A 5-Step AI TRiSM Approach to AI Governance
Fortunately, there are ways that enterprises looking to enable the safe use of AI can integrate AI models into their data landscape while meeting legal requirements, upholding ethical standards, and driving positive business outcomes. Here’s how incorporating AI governance into a central Data Command Center enables the safe use of AI.