What are the two types of consent regimes?
When it comes to relying on a user’s consent as a lawful basis of data processing, global privacy regulations can be classified as either an opt-in or opt-out consent regime.
Opt-in consent
In an opt-in consent regime, user consent is required before processing their personal data, and users are explicitly asked to provide their consent and they are free to grant or deny consent. Some of the examples of opt-in consent regimes are the European Union, Brazil, and New Zealand.
Opt-out consent
In an opt-out consent regime, the user’s consent is not required before the processing of personal data. However, organizations are still required to provide users an option to object to the processing of their data and provide relevant information about the use of cookies. Some of the examples of opt-out consent regimes are the United States, Hong Kong, and Estonia.
Is European Union an opt-in consent regime?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and e-Privacy Directive are two major laws that govern the use of cookies and other tracking technologies in the European Union (EU).
The EU’s data privacy legal framework requires data controllers to obtain opt-in consent where the data processing is based on the data subject’s consent.
The GDPR defines consent of the data subject as “any freely given, specific, informed and unambiguous indication of the data subject’s wishes by which he or she, by a statement or by a clear affirmative action, signifies agreement to the processing of personal data belonging to him or her”.
Although the GDPR does not expressly mention cookies, it classifies cookies as a type of “online identifier” meaning that cookies may be considered personal data under certain circumstances. As a result, all GDPR principles pertaining to the processing of personal data will automatically apply to the use of cookies and other similar tracking technologies.
The e-Privacy Directive further requires organizations making use of cookies and similar tracking technologies to provide clear and precise information to users about the purposes of cookies and provide users an opportunity to refuse to have a cookie stored on their terminal equipment.
Read about EDPB’s Updated Guidelines on Consent here.
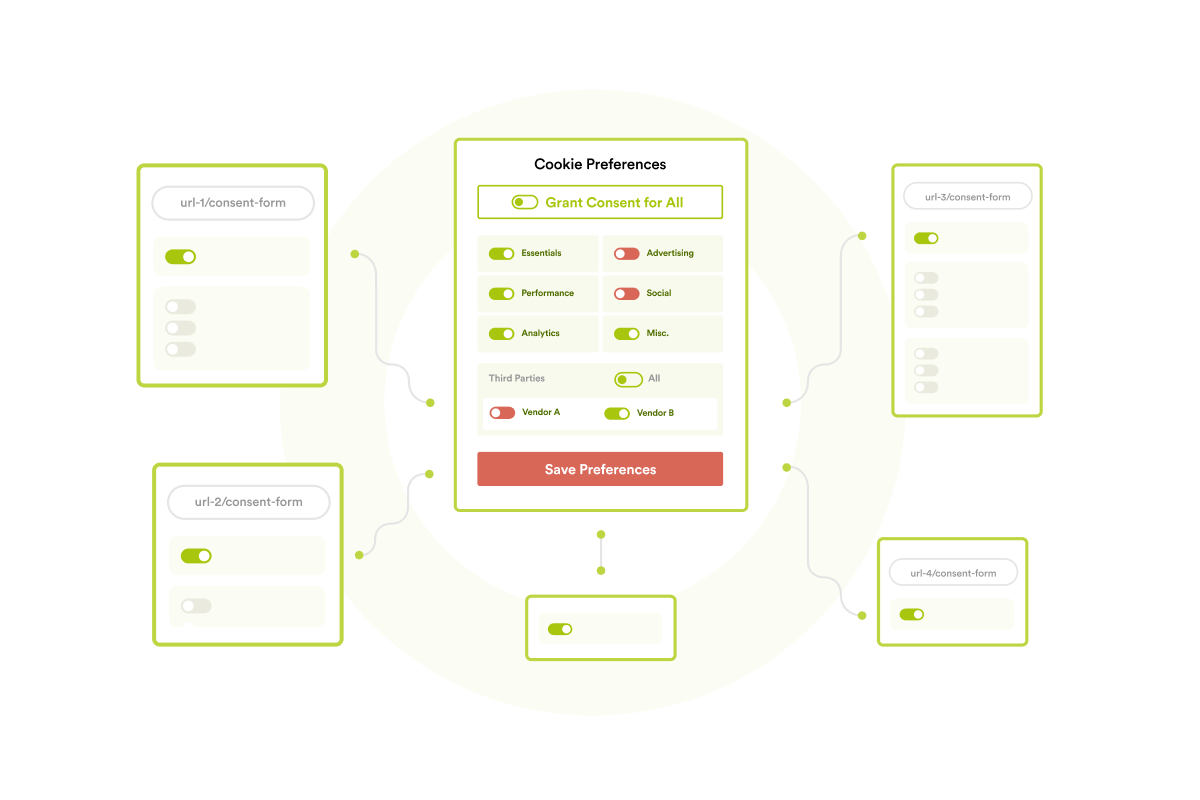
How do organizations collect user consent?
Organizations subject to GDPR and e-Privacy Directive must ensure that the cookie consent banner includes the following:
- Clear and comprehensive information about cookies:
The cookie consent banner must contain plain and understandable information about the cookies that an organization intends to use. The information must include at least, the information on the general purposes of cookies, the user’s ability to withdraw and change consent along with the method of doing so, the data controller’s name and identity, data processors’ names and identities, full list of recipients or categories of recipients who will obtain personal data through the processing of cookies, and information on individual cookie properties.
- User’ ability to withdraw and change the consent:
The cookie consent banner must give equal prominences to accept and reject options. The user must be allowed to withdraw consent or change consent at any time, without any detriment in a user-friendly mechanism.
- Selection and deselection of individual cookies:
The cookie consent banner must allow the selection and deselection of individual cookies by purposes and must have separate opt-in and opt-outs for separate types of cookies.
- No pre-selected checkboxes or cookie walls:
The cookie consent banner must not have pre-selected preferences by default for non-essential cookies. Similarly, an organization must not make access to a service or functionality of a website conditional on the user’s consent to the processing of non-essential cookies. This means the use of cookie walls is prohibited.
These requirements help organizations ensure consent is freely given, specific, informed, and an unambiguous indication of users’ preferences.
Additionally, organizations must maintain up-to-date and comprehensive cookie consent records. These records must include information provided to users at the time of obtaining their consent, information of the session in which consent was expressed, consent workflow at the time of the session including subject identity, cookie category, consent status, consent date, and information on first and third parties of cookies.